Computer components like the CPU, motherboard, computer case, RAM and drive are the core of a computer. They determine the capabilities and features of a computer, as well as its power and processing speeds. It’s important to choose computer components that can work together to satisfy your needs. The computer motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) where most computer components are connected. It provides connectivity between the computer hardware components, for instance, the processor (CPU), memory (RAM), hard drive, and video card.
Computer Components
In order to operate a computer the following parts are required.
Mouse – This is small device that will allow you to make selections on your computer screen. They come in different shapes and sizes but resemble a mouse. It connects to the system unit or can be wireless. The mouse can have 1 button, 2 buttons, 3 buttons, or 3 buttons and a scroll button. Most PCs now have a mouse with 2 buttons and a 'scroll' button in the center.
Keyboard – This is used for typing text onto the computer screen. It resembles a typewriter and has special keys that do certain things.
Monitor – This is where you will find your computer screen and where information is displayed. It resembles a television screen and can show both still or moving images.
Computer Accessories
Many additional accessories are available for computers and although these are not required, they can come in handy depending on what you're going to use your computer for. For example, if you plan on printing, you will need a printer--but it is not required to make the computer run.
Network Card – If you want to connect to a Local Area Network (LAN) or the Internet, you'll need this card (or a modem). This works by receiving and sending information (data packets) over a local network or from/to the internet using a high speed cable line.
Modem –This works like a network card, only it's much slower and uses a standard phone line to communicate to the outside world.Printer – This is used for transferring data from the PC and printing it on a piece of paper. Printers can print in either black and white or color.
Scanners – These are similar to printers however, they can scan images that can either be viewed on the monitor screen or printed out. There are also scanners/printer combinations that print and scan using one machine.
Speakers – These are used to play sound. They can either be built-in or connected by using cables.
Webcam – This is a camera that can be used with your computer that will allow you to communicate with others who have webcams. You can also take photos and record videos with a webcam.
Setting Up – Avoiding Need for Repair
Desk/Table – Before putting your computer on a desk or table make sure it is set up near an electrical outlet and network/phone jack. You will need the outlet for power and the network/phone jack if you plan on using the internet.
Removing the Equipment – You will want to be very careful removing the equipment out of the box because all the pieces to a computer are fragile and breaking them will create additional costs. As you unpack the computer, be sure you have all the required parts. Some of the parts include a power cord, monitor and more. If it is a new computer it will come with a manual so be sure to save it. Remember, this is a computer. You don't want to zap it with static electricity. You do not want to have strong magnets near it. You don't want to put it in a place that floods frequently.
Position – You will want to position the computer and its parts so that they are conveniently accessible. The keyboard should be reachable, the tower should be well-ventilated, the monitor should be in full view and the mouse should be set up depending on which hand you plan on using.
Plug-in – Once the layout of the computer has been sorted out, it is time to plug in all the computer parts. These parts are usually color-coded and will be plugged into the back of the tower. Refer to your user manual if you are unsure how to plug something in. Connect the monitor to the computer. Usually the monitor cable is uniquely shaped because of it's little hand-screws that will need to be tightened once plugged in.

Other Accessories – Next, plug in the accessories to your computer such as the modem, speakers, microphone and any other accessories you have such as the printer. Be sure to follow the instructions that came along with the each device because every device is different and will have different instructions.
Power Up – Once everything has been plugged in and you double-checked the connections, you can turn on the computer. Once it boots up, instructions will appear on the screen on how to complete the installation. Follow the directions.
Keywords
CD-ROM Drive – This is a part of a computer that reads information stored on compact discs. It is usually found with the system unit/tower.
Click – A 'click' is how you select an item on the monitor/screen. In order to click the option you would like to choose, press and release the left mouse button.

Internet – This is a global system that serves billions of people across the world. It is used to connect computer networks and includes all sorts of uses from businesses to personal use. It carries information including electronic mail and instant messaging. It can also be used for online shopping, taking classes, locating a business, social networking and much more.
When a computer 'freezes' this means that it has completely stopped responding. As you try to move the mouse around the monitor it will appear jammed and the mouse arrow will not move. This issue can be caused by several different things such as a virus attack, maxed out memory, outdated hardware drivers and more. There are ways to get out of a 'frozen' screen which includes hitting certain keys or rebooting the entire system.
Rebooting a Frozen Computer – If the 'End Task' option has not helped your computer to recover you will need to shut it down or reboot it. Keep in mind that whatever documents were not saved will be completely lost from the shut down or reboot process. To shut it down or reboot it, hit the CTRL + ALT + DEL buttons all at one time and choose the option that you desire (Power Off, Restart, etc.). If that is completely unresponsive, you have no choice, hit the power button to turn the computer off. Wait 60 seconds. Now turn it back on.
Issue in Software – It could be that the computer is locking up because of a problem with the software. If you find the computer freezes while running a particular program, check to see if any updates are available for that particular software. Also check updates available for your operating system as well.
Hardware Issues – If a hardware issue is causing the computer to freeze it could be so many things--bad memory, overheating chip, hard drive errors, video card problems, etc. Hardware can be tested by swapping out the bad parts for good ones. To do this you may need a computer service.
Program Stops Responding
When a program on a computer stops responding it may be caused by several different things such as a problem with hardware or software, lack of resources or a bug in the drivers or software. You can tell if the computer has stopped responding by moving the mouse arrow and pressing buttons. If nothing happens, then the program is not responding. To recover from any program that has stopped responding you will need to end the current task.
Ending/Terminating a Task – To end a task or program hit the CTRL + ALT + DEL keys on the keyboard all together at one time. Click the 'Close Program' option or go to the 'Task Manager' window. Once you get to the 'Task Manager' window, click the 'End Task' option. Keep in mind that all information that has not been saved will be lost when you end a program.
Keywords
Bug – Different from a computer virus, a bug is an issue or error in a computer program. When software is developed, sometimes the programmers do not anticipate all the environments the software will run in that may cause the program to become unstable. These issues are reported back to the company by users like you. The company then provides 'fixes' or 'patches' to correct these errors. That's why it is important to always look at your software manufacture's website for the latest updates.
CPU – This stands for Central Processing Unit and is also known as a processor. Its function is to handle the instructions and calculations that it gets from other computer components such as hardware and software.
Hardware Driver – A hardware driver is a software program that tells the computer how to use a piece of hardware. Every component of a computer will have a hardware driver such as a printer, hard disk, DVD player and more. 'Hardware Driver' sounds like it's hardware, but it's not. It's software--the software that runsthe actual hardware.
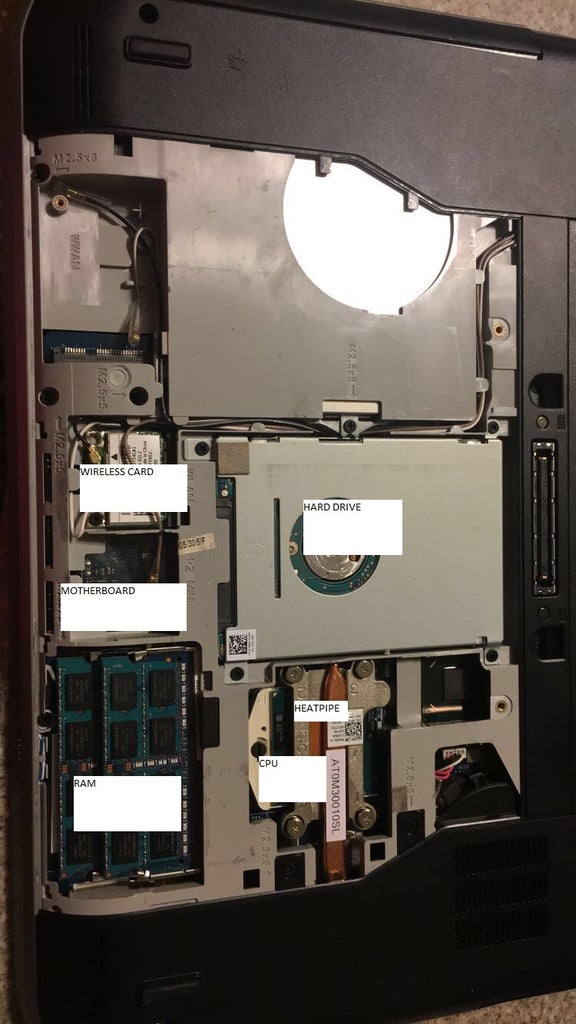


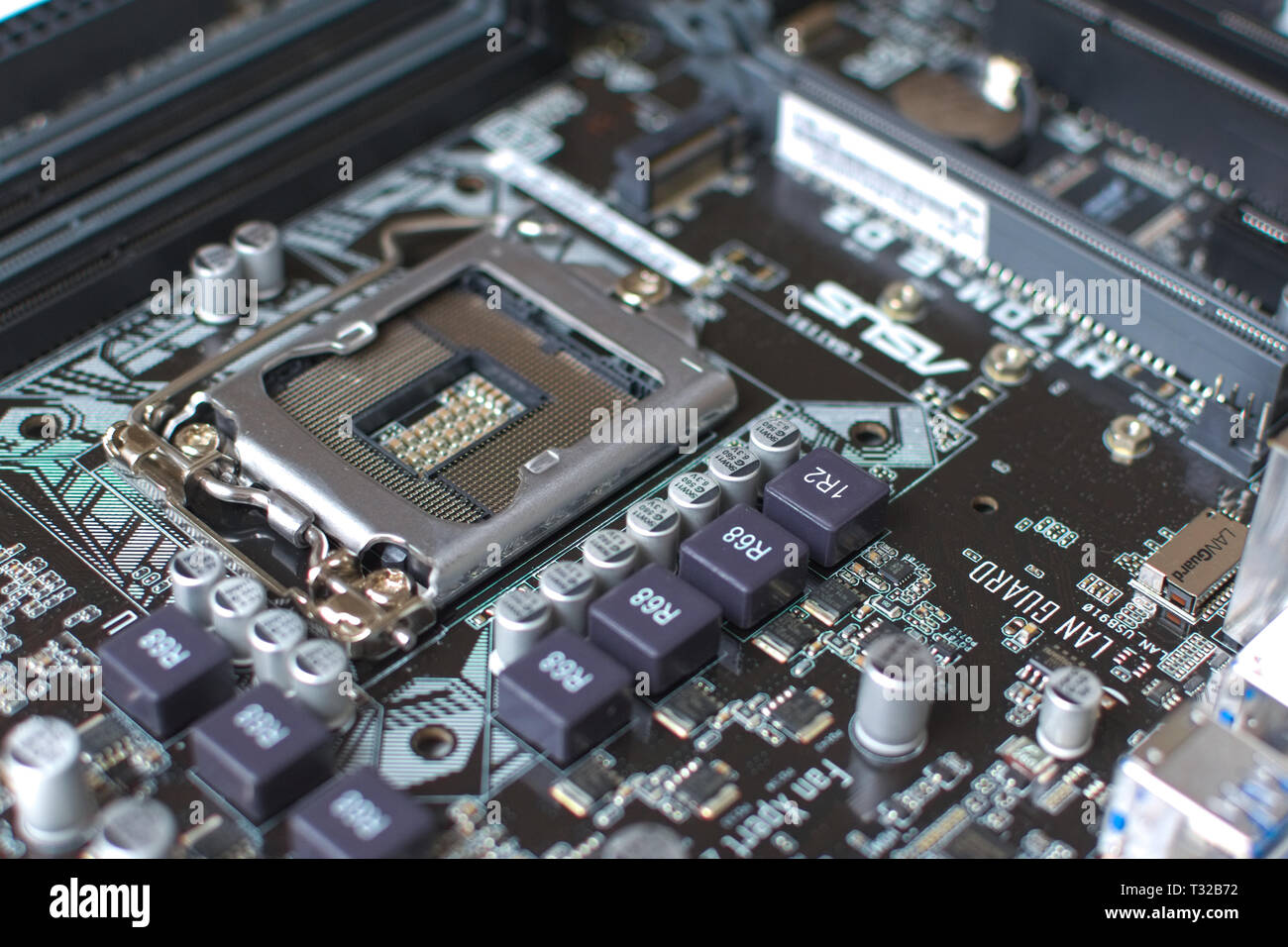
Motherboard – Found within a computer system, a motherboard is the 'board' that interconnects all internal and external components of a computer.
Num Lock LED – LED stands for Light Emitting Diode and it is a light that is either red/amber or green in color. It indicates whether or not the Num Lock button is on or off.
RAM – This stands for Random Access Memory and is used to describe a computer's memory. It is also referred to as just 'memory' or 'main memory' or 'system memory'. It requires power and if the power is not supplied, data can be lost. It is different than a hard drive. The hard drive is where permanent data is stored. RAM is where run-time programs reside for quick and instant access to the CPU.
Task – This is what the computer is currently working on. For example, if it is printing or running a program, this is a task that the computer is running.
A computer is the sum of it’s parts. One part alone doesn’t make a computer. Typically the primary hardware components that make up a computer is the CPU (Central Processing Unit), Memory (main memory), Storage Devices (like flash drives, cds, HDD), Input Devices (keyboard & mouse), Output Devices (i.e. Monitors and Printers), and Communication devices (i.e. modems and network interface cards).
A computer parts are interconnected by the bus. A bus is a system or roads that run from one component to another, allowing data & power able to reach all the components. For personal computers, the bus is built into the Motherboard.
Table of Contents
- 5 Computer Storage & Memory
A motherboard is a circuit case that connects all the parts of a computer together. Motherboards can be monolithic or modular. Monolithic refers to motherboards that don’t give you the option of customizing internal parts (like Macs). Modular refers to motherboards that allow you to customize and swap parts (Dell).
BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System. Bios is the software embedded in a chip on the motherboard. This Software is responsible for checking the memory, processor, and other components are functioning properly before the PC boots up. Error Checking done by Bios is called POST (Power On Self Test). POST is recognized as beeps. BIOS also tells the computer how to turn on.
Stores setting data from the BIOS -or- Can mean the same as BIOS. Resets when CMOS battery is removed.
The CPU stands for the Central Processing Unit. The CPU is the computer’s brain, so to speak. It retrieves instructions from the memory and executes them.
The CPU usually has two components: a control unit and an arithmetic/logic unit. The control unit controls and coordinates the actions of the other components. The arithmetic/logic unit performs numeric operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and logical operations.
Today’s CPUs are built on small silicon semiconductor chips that contain millions of tiny electric switches, called transistors, for processing information.
Every computer has an internal clock, which emits electronic pulses at a constant rate. These pulses are used to control and synchronize the CPU’s pace of operations. A higher clock speed enables more instructions to be executed in a given period of time. The unit of measurement of clock speed is the hertz (Hz), with 1 hertz equaling 1 pulse per second.
Motherboard Components Pdf
Most modern CPUs are microprocessors, meaning they are contained on a single integrated circuit (IC) chip. An IC that contains a CPU may also contain memory, peripheral interfaces, and other components of a computer; such integrated devices are variously called microcontrollers or systems on a chip (SoC). Some computers employ a multi-core processor, which is a single chip containing two or more CPUs called “cores”; in that context, single chips are sometimes referred to as “sockets”. Array processors or vector processors have multiple processors that operate in parallel, with no unit considered central.
CPU prioritizes data retrieval like so: L1 > L2 > L3 > RAM > Hard drive
Motherboard Components And Functions
In computing, memory refers to the computer hardware devices used to store information for immediate use in a computer; it is synonymous with the term “primary storage”. Computer memory operates at a high speed, for example random-access memory (RAM), as a distinction from storage that provides slow-to-access program (HD drive) and data storage but offers higher capacities. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to secondary storage, through a memory management technique called “virtual memory”.
Most semiconductor memory is organized into memory cells or bistable flip-flops, each storing one bit (0 or 1). Flash memory organization includes both one bit per memory cell and multiple bits per cell (called MLC, Multiple Level Cell). The memory cells are grouped into words of fixed word length, for example 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 or 128 bit. Each word can be accessed by a binary address of N bit, making it possible to store 2 raised by N words in the memory. This implies that processor registers normally are not considered as memory, since they only store one word and do not include an addressing mechanism.
Memory is often associated with addressable semiconductor memory, i.e. integrated circuits consisting of silicon-based transistors, used for example as primary storage but also other purposes in computers and other digital electronic devices. There are two main types of semiconductor memory, volatile and non-volatile. Examples of non-volatile memory are flash memory (used as secondary memory) and ROM, PROM, EPROM and EEPROM memory (used for storing firmware such as BIOS). Examples of volatile memory are primary storage (typically dynamic RAM, DRAM), and fast CPU cache memory (typically static RAM, SRAM, which is fast but energy-consuming and offer lower memory capacity per area unit than DRAM).
Cache Memory
Note that Cache memory is the fastest memory, and is closely situated to the CPU for efficiency (less time taken for signal to reach CPU).
RAM
Computer Hardware Motherboard
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a form of computer data storage that allows for changes to stored data (in contrast to ROM). In other words, RAM is re-writable, and ROM is not. RAM is a type of volatile memory, meaning the data stored is lost if the power is removed.
HDD
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a computer data storage device. It contrasts from RAM & other memory by storing data for long periods of time without loss, and not losing data when the power is removed. HDD uses rapidly rotating disks that are coated with magnetic material. This magnetic material store changes applied to it by the magnetic heads; this is how data is “etched” onto the Hard Disk Drive.
ROM
ROM, or Read-Only Memory,is a type of non-volatile memory. Read-Only means that you cannot make changes to the stored data on the memory. Non-volatile means that the data on the memory is not erased when the computer is turned off. Typically, ROM is used to store instructions that are required to start a computer. These instructions are called bootstrap.
Network Router is a networking device that delivers data packets between computers on a network. Routers can connect multiple networks together for computers to communicate through.
Network Switch is just like a router, except the Switch only connects data lines from one single Network. Router connects multiple networks. …
Computer Hardware1.motherboard Components The Mechanical
Takeaway: Router can connect multiple networks, Switch only connects a single network.
Switch vs Router
A Switch functions by moving/forwarding data frames based on MAC address. This happens at that lower level of the network in what is known as Layer 2 (Data link layer) of the OSI Model. When communications happen it is from MAC address to MAC Address, or hardware to hardware
A Router functions by moving/routing data packets based on IP address. This happens a little higher in the network in what is known as Layer 3 (Network layer) of the OSI Model. When communications happen here it is from IP address to IP address.
Computer Motherboard Components
Network Card is an electronic device that connects a computer to a Network.
